 Programming Interfaces Guide
Programming Interfaces Guide
 CHAPTER 2. The Embedded SQL Interface
CHAPTER 2. The Embedded SQL Interface
Fetching data in Embedded SQL is done using the SELECT statement. There are two cases:
The SELECT statement returns at most one row.
The SELECT statement may return multiple rows.
 Embedded SELECT
Embedded SELECTA single row query retrieves at most one row from the database. A single-row query SELECT statement has an INTO clause following the select list and before the FROM clause. The INTO clause contains a list of host variables to receive the value for each select list item. There must be the same number of host variables as there are select list items. The host variables may be accompanied by indicator variables to indicate NULL results.
When the SELECT statement is executed, the database server retrieves the results and places them in the host variables. If the query results contain more than one row, the database server returns an error.
If the query results in no rows being selected, a Row Not Found warning is returned. Errors and warnings are returned in the SQLCA structure, as described in The SQL Communication Area.
For example, the following code fragment returns 1 if a row from the employee table is successfully fetched, 0 if the row doesn't exist and -1 if an error occurs.
EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION;
long emp_id;
char name[41];
char sex;
char birthdate[15];
short int ind_birthdate;
EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION;
. . .
int find_employee( long employee )
{
emp_id = employee;
EXEC SQL SELECT emp_fname ||
' ' || emp_lname, sex, birth_date
INTO :name, :sex,
birthdate:ind_birthdate
FROM "dba".employee
WHERE emp_id = :emp_id;
if( SQLCODE == SQLE_NOTFOUND ) {
return( 0 ); /* employee not found */
} else if( SQLCODE < 0 ) {
return( -1 ); /* error */
} else {
return( 1 ); /* found */
}
}
 Cursors in Embedded SQL
Cursors in Embedded SQLA cursor is used to retrieve rows from a query that has multiple rows in its result set. A cursor is a handle or an identifier for the SQL query and a position within the result set.
 For an introduction to cursors, see Working with cursors.
For an introduction to cursors, see Working with cursors.
 To manage a cursor in Embedded SQL:
To manage a cursor in Embedded SQL:Declare a cursor for a particular SELECT statement, using the DECLARE statement.
Open the cursor using the OPEN statement.
Retrieve results one row at a time from the cursor using the FETCH statement.
Fetch rows until the Row Not Found warning is returned.
Errors and warnings are returned in the SQLCA structure, described in The SQL Communication Area.
Close the cursor, using the CLOSE statement.
By default, cursors are automatically closed at the end of a transaction (on COMMIT or ROLLBACK). Cursors that are opened with a WITH HOLD clause are kept open for subsequent transactions until they are explicitly closed.
The following is a simple example of cursor usage:
void print_employees( void )
{
int status;
EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION;
char name[50];
char sex;
char birthdate[15];
short int ind_birthdate;
EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION;
EXEC SQL DECLARE C1 CURSOR FOR
SELECT emp_fname || ' ' || emp_lname,
sex, birth_date
FROM "dba".employee;
EXEC SQL OPEN C1;
for( ;; ) {
EXEC SQL FETCH C1 INTO :name, :sex, :birthdate:ind_birthdate;
if( SQLCODE == SQLE_NOTFOUND ) {
break;
} else if( SQLCODE < 0 ) {
break;
}
if( ind_birthdate < 0 ) {
strcpy( birthdate, "UNKNOWN" );
}
printf( "Name: %s Sex: %c Birthdate:
%s.n",name, sex, birthdate );
}
EXEC SQL CLOSE C1;
}
 For complete examples using cursors, see Static cursor example, and Dynamic cursor example.
For complete examples using cursors, see Static cursor example, and Dynamic cursor example.
A cursor is positioned in one of three places:
On a row
Before the first row
After the last row
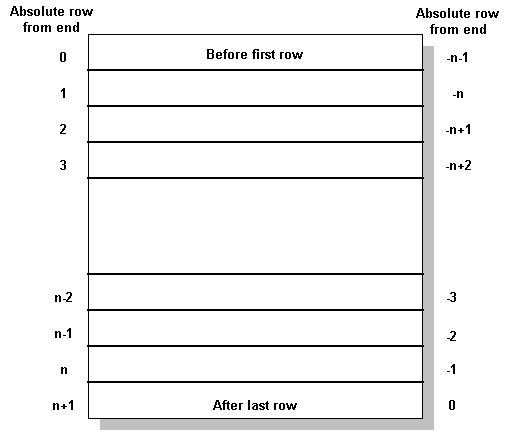
When a cursor is opened, it is positioned before the first row. The cursor position can be moved, using the FETCH command (see FETCH statement ). It can be positioned to an absolute position either from the start or from the end of the query results. It can also be moved relative to the current cursor position.
There are special positioned versions of the UPDATE and DELETE statements that can be used to update or delete the row at the current position of the cursor. If the cursor is positioned before the first row or after the last row, a No Current Row of Cursor error is returned.
The PUT statement can be used to insert a row into a cursor.
Inserts and some updates to DYNAMIC SCROLL cursors can cause problems with cursor positioning. The database server does not put inserted rows at a predictable position within a cursor unless there is an ORDER BY clause on the SELECT statement. In some cases, the inserted row does not appear at all until the cursor is closed and opened again.
With Adaptive Server Anywhere, this occurs if a temporary table had to be created to open the cursor (see Temporary tables used in query processing for a description).
The UPDATE statement may cause a row to move in the cursor. This happens if the cursor has an ORDER BY clause that uses an existing index (a temporary table is not created).
