 User's Guide
User's Guide
 PART 1. Working with Databases
PART 1. Working with Databases
 CHAPTER 1. Running the Database Server
CHAPTER 1. Running the Database Server
When you log on to a computer using a user ID and a password, you establish a session. When you start a database server, or any other application, it runs within that session. When you log off the computer, all applications associated with the session terminate.
It is common to require database servers to be available all the time. To make this easier, you can run Adaptive Server Anywhere for Windows NT and for UNIX in such a way that, when you log off the computer, the database server does not terminate. The way you do this depends on the operating system you are using.
Windows NT service You can run the Windows NT database server as a service. This has many convenient properties for running high availability servers.
UNIX daemon You can run the UNIX database server as a daemon by using the -ud command-line option. This enables the database server to run in the background, and to continue running after you log off.
 Running the UNIX database server as a daemon
Running the UNIX database server as a daemonIn order to run the UNIX database server in the background, and to enable it to run independently of the current session, you run it as a daemon.
Do not use & to run the database server in the background |
 To run the UNIX database server as a daemon:
To run the UNIX database server as a daemon:Use the -ud command-line option when starting the database server. For example:
dbsrv6 -ud asademo.db
 Understanding Windows NT services
Understanding Windows NT servicesAlthough the database server can be run like any other Windows NT program rather than as a service, there are limitations to running it as a standard program, particularly in multi-user environments.
When you start a program, it runs under your Windows NT login session: if you log off the computer, the program terminates. Only one person can be logged on to Windows NT (on any one computer) at one time. This restricts the use of the computer if you wish to keep a program running much of the time, as is commonly the case with database servers. You must stay logged in to the computer running the database server in order for the database server to keep running. This can also present a security risk as the Windows NT computer must be left in a logged on state.
Installing an application as a Windows NT service enables it to run even when you log off.
When you start a service, it logs on using a special system account called LocalSystem (or using another account you specify). The service is not tied to the user ID of the person starting it, and therefore is not stopped when that person logs off. A service can also be configured to start automatically when the NT computer is started, before a user logs on.
Sybase Central provides a more convenient and comprehensive way of managing Adaptive Server Anywhere services than the Windows NT services manager.
 Programs that can be run as Windows NT services
Programs that can be run as Windows NT servicesThe following programs can be run as services:
The network server (dbsrv6.exe).
The personal server (dbeng6.exe).
The Adaptive Server Anywhere Replication Agent (dbltm.exe: available separately).
The SQL Remote Message Agent (dbremote.exe).
A sample application.
Not all these applications are supplied in all editions of Adaptive Server Anywhere.
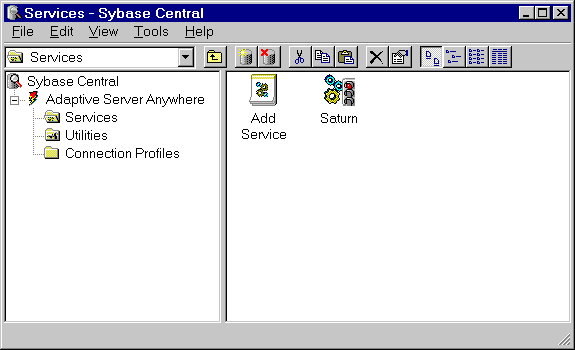
 Managing services
Managing servicesThis section describes how to manage services. You can carry out the following service management tasks from Sybase Central:
Add, edit, and remove services.
Start, stop, and pause services.
Modify the parameters governing a service.
Add databases to a service, so that you can run several databases at one time.
The service icons in Sybase Central display the current state of each service using a traffic light icon (running, paused, or stopped).
 Adding a service
Adding a serviceThis section describes how to set up services using Sybase Central.
 To add a new service:
To add a new service:In Sybase Central, open the Services folder.
Double-click Add Service. The Service Creation Wizard is displayed.
Follow the instructions in the wizard to define the service you are creating.
Service Names must be unique within the first eight characters.
If you choose to start a service automatically, it will start whenever the computer starts Windows NT. If you choose to start manually, you need to start the service from Sybase Central each time. You may want to select Disabled if you are setting up a service for future use.
In the window, enter command-line switches for the executable, without the executable name itself. For example, if you wish a network server to run using the sample database with a cache size of 20Mb, and a name of myserver, you would enter the following in the Parameters box:
-c 20M -n myserver c:\asa6\asademo.db
Line breaks are optional. For information on valid command-line switches, see the description of each program in Database Administration Utilities.
Choose the account under which the service will run: the special LocalSystem account or another user ID. For more information about this choice, see Setting the account options.
If you want the service to be accessible from the Windows NT desktop, check Allow Service to Interact with Desktop. If this option is unchecked, no icon or window appears on the desktop.
 For more information on the configuration options, see Configuring services.
For more information on the configuration options, see Configuring services.
 Removing a service
Removing a serviceRemoving a service removes the server name from the list of services. Removing a service does not remove any software from your hard disk.
If you wish to re-install a service that you have removed, you will need to reenter the command-line switches.
 To remove a service:
To remove a service:In Sybase Central, open the Services folder.
Right-click the icon of the service you wish to remove, and select Delete from the popup menu
 Configuring services
Configuring servicesA service runs a database server or other application with a set of command-line switches. For a full description of the command-line switches for each of the administration utilities, see Database Administration Utilities.
In addition to the command-line switches, services accept other parameters that specify the account under which the service will run and the conditions under which it will start.
 To change the parameters for a service:
To change the parameters for a service:In Sybase Central, open the Services folder.
Right-click the icon of the service whose parameters you wish to change in the right panel of Sybase Central, and select Properties from the popup menu.
Alter the parameters as needed in the tabs of the Property sheet.
When you have altered the parameters as you wish, click OK to accept and save the changes.
Changes to a service configuration do not take effect immediately. They take effect next time the service is started. The Startup option is applied the next time Windows NT is started.
 Setting the startup option
Setting the startup optionThe following options govern startup behavior for an Anywhere service:
Automatic If you choose the Automatic setting, the service starts whenever the Windows NT operating system is started on the computer. This setting is appropriate for database servers and other applications that are run all the time.
Manual If you choose the Manual setting, the service starts only when a user with Administrator permissions starts it. For information about Administrator permissions, see your Windows NT documentation.
Disable If you choose the Disable setting, the service will not start.
 Entering command-line switches
Entering command-line switchesThe Configuration tab of the service property sheet provides a text box for entering command-line switches for a service. Do not enter the name of the program executable in this box.
To start a network server service running two databases, with a cache size of 20 Mb, and with a name of my_server, enter the following in the Parameters box:
-c 20M -n my_server c:\asa6\db_1.db c:\asa6\db_2.db
To start a SQL Remote Message Agent service, connecting to the sample database as user ID DBA, enter the following:
-c "uid=dba;pwd=sql;dbn=asademo"
The following figure illustrates a sample Property sheet.
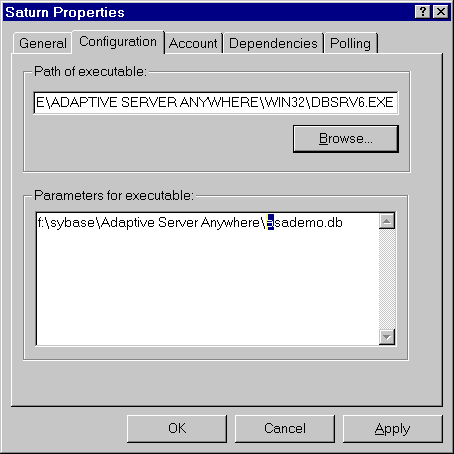
 The command-line switches for a service are the same as those for the executable. For a full description of the command-line switches for each program, see The Database Server.
The command-line switches for a service are the same as those for the executable. For a full description of the command-line switches for each program, see The Database Server.
 Setting the account options
Setting the account optionsYou can choose under which account the service will run. Most services run under the special LocalSystem account, and this is the default option for services. You can set the service to log on under another account by clicking Account and entering the account information.
If you choose to run the service under an account other than LocalSystem, that account must have the "log on as a service" privilege. This can be granted from the Windows NT User Manager application, under Advanced Privileges.
Whether or not an icon for the service appears on the taskbar or desktop depends on the account that is selected, and whether Allow Service to Interact with Desktop is checked, as follows:
If a service is running under LocalSystem, and Allow Service to Interact with Desktop is checked in the Service Configuration window, an icon appears on the desktop of every user logged in to NT on the computer running the service. Consequently, any user can open the application window and stop the program that is running as a service.
If a service is running under LocalSystem, and Allow Service to Interact with Desktop is unchecked in the Service Configuration window, no icon appears on the desktop for any user. Only users with permissions to change the state of services can stop the service.
If a service is running under another account, no icon appears on the desktop. Only users with permissions to change the state of services can stop the service.
 Changing the executable file
Changing the executable fileTo change the program executable file associated with a service, click the Configuration tab on the service property sheet and enter the new path and file name in the Path of Executable box.
If you move an executable file to a new directory, you must modify this entry.
 Adding new databases to a service
Adding new databases to a serviceEach network server or personal server can run more than one database. If you wish to run more than one database at a time, we recommend that you do so by attaching new databases to your existing service, rather than by creating new services.
 To add a new database to a service:
To add a new database to a service:Double-click the server to change the parameters for the service, and click the configuration tab.
Add the filename of the new database to the end of the list of parameters.
Click OK to save the changes.
The new database will not be added to the service immediately. It is loaded the next time the service is started.
Databases can be started on running servers by client applications, such as Interactive SQL.
 For a description of how to start a database on a server from Interactive SQL, see START DATABASE statement. For a description of how to implement this function in an Embedded SQL application, see the db_start_database function in The Embedded SQL Interface. Starting a database from an application does not attach it to the service. If the service is stopped and restarted, the additional database will not be started automatically.
For a description of how to start a database on a server from Interactive SQL, see START DATABASE statement. For a description of how to implement this function in an Embedded SQL application, see the db_start_database function in The Embedded SQL Interface. Starting a database from an application does not attach it to the service. If the service is stopped and restarted, the additional database will not be started automatically.
 Setting the service polling frequency
Setting the service polling frequencySybase Central polls at specified intervals to check the state (started, stopped, paused, removed) of each service, and updates the icons to display the current state.
 To alter the Sybase Central polling frequency:
To alter the Sybase Central polling frequency:In Sybase Central, open the Services folder.
Right-click the icon of any service in the right panel of Sybase Central, and select Polling from the popup menu.
Set the polling frequency. The frequency applies to all services, not just the one selected.
The value you set in this window is saved for subsequent sessions, until you change it.
 Starting, stopping, and pausing services
Starting, stopping, and pausing services To start, stop, or pause a service:
To start, stop, or pause a service:In Sybase Central, open the Services folder.
Right-click the icon of the service.
Select Start, Stop, or Pause from the popup menu
If you start a service, it keeps running until you stop it. Closing Sybase Central or logging off will not stop the service.
Stopping a service closes all connections to the database and unloads the database server. For other applications, the program is closed down.
Pausing a service prevents any further action being taken by the application. It does not shut the application down or (in the case of server services) close any client connections to the database. Most users will not need to pause their services.
 The Windows NT Service Manager
The Windows NT Service ManagerYou can use Sybase Central to carry out all the service management for Adaptive Server Anywhere. You do not need to use the Windows NT Service Manager in the Control Panel.
If you open the Windows NT Service Manager (from the Windows NT Control Panel), a list of services is given. The names of the Adaptive Server Anywhere services are formed from the Service Name you provided when installing the service, prefixed by Adaptive Server Anywhere. All the services you have installed will be found together in the list.
You cannot install or configure parameters for Adaptive Server Anywhere services using the NT Service Manager. You must use Sybase Central.
 Running more than one service
Running more than one serviceThis section describes some topic specific to running more than one service at a time.
 Service dependencies
Service dependenciesIn some circumstances you may wish to run more than one executable as a service, and these executables may depend on each other. For example, you may wish to run a server and a SQL Remote Message Agent or Log Transfer Manager to assist in replication.
In cases such as these, the services must start in the proper order. If a SQL Remote Message Agent service starts up before the server has started, it will fail because it cannot find the server.
You can prevent these problems using service groups. You can manage the service groups from Sybase Central.
 Service groups overview
Service groups overviewYou can assign each service on your system to be a member of a service group. By default, each service belongs to a group, as listed in the following table.
Service |
Default group |
|---|---|
Network server |
SQLANYServer |
Personal server |
SQLANYEngine |
SQL Remote Message Agent |
SQLANYRemote |
Replication Agent |
SQLANYLTM |
Before you can configure your services to ensure that they start in the correct order, you must check that your service is a member of an appropriate group. You can check which group a service belongs to, and change this group, from Sybase Central.
 To check and change which group a service belongs to:
To check and change which group a service belongs to:In Sybase Central, open the Services folder.
Right-click the icon of the service you wish to start, and select Properties from the popup menu.
Click the Dependencies tab. The text box displays the name of the group to which the service belongs.
Click Look Up to display a list of available groups on your system.
Select one of the groups, or type a name of a new group, and click OK to assign the service to that group.
 Managing service dependencies
Managing service dependenciesWith Sybase Central you can specify the following types of dependency for a service.
You can ensure that at least one member of a each of a list of service groups has started before the current service
You can ensure that each of a list of services, has started before the current service.
For example, you may wish to ensure that a particular network server has started before a SQL Remote Message Agent that is to run against that server starts.
 To add a service or group to a list of dependencies:
To add a service or group to a list of dependencies:In Sybase Central, open the Services folder.
Right-click the icon of the service, and select Properties from the popup menu.
Click the Dependencies tab. Click Add Service or Add Group to add a service or group to the list of dependencies.
Select one of the services or groups from the list, and click OK to add the service or group to the list of dependencies.
 Possible problems running more than one server as a service
Possible problems running more than one server as a serviceYou may experience problems if you run more than one network server as a service at a time. Under some circumstances, it cannot be guaranteed that the correct service will respond to a client that sends a request to the database server as a broadcast. Broadcasts are typically used if you are using TCP/IP, or IPX on a Novell network without using the bindery. The broadcast is only used to find the server during startup.
We recommend that you not run more than one network server service at a time.
