 User's Guide
User's Guide
 PART 5. The Adaptive Server Family
PART 5. The Adaptive Server Family
 CHAPTER 31. Adaptive Server Anywhere as an Open Server
CHAPTER 31. Adaptive Server Anywhere as an Open Server
Adaptive Server Anywhere can communicate with other Adaptive Servers, Open Server applications, and client software on the network. Clients can talk to one or more servers, and servers can communicate with other servers via remote procedure calls. In order for products to interact with one another, each needs to know where the others reside on the network. This network service information is stored in the interfaces file.
 The interfaces file
The interfaces fileThe interfaces file is usually named sql.ini on PC operating systems and interfaces, or interfac on UNIX operating systems.
The interfaces file is like an address book. It lists the name and address of every database server known to Open Client applications on your machine. When you use an Open Client program to connect to a database server, the program looks up the server name in the interfaces file and then connects to the server using the address.
The name, location, and contents of the interfaces file differ between operating systems. Also, the format of the addresses in the interfaces file differs between network protocols.
When you install Adaptive Server Anywhere, the setup program creates a simple interfaces file that you can use for local connections to Adaptive Server Anywhere over TCP/IP. It is the System Administrator's responsibility to modify the interfaces file and distribute it to users so that they can connect to Adaptive Server Anywhere over the network.
 Using the DSEDIT utility
Using the DSEDIT utilityThe dsedit utility is a Windows 95 and Windows NT utility that allows you to configure the interfaces file (sql.ini). The following sections explain how to use the dsedit utility to configure the interfaces file.
 These sections describe how to use dsedit for those tasks required for Adaptive Server Anywhere. It is not complete documentation for the dsedit utility. For more information on dsedit, see the Utility Programs book for your platform, included with other Sybase products.
These sections describe how to use dsedit for those tasks required for Adaptive Server Anywhere. It is not complete documentation for the dsedit utility. For more information on dsedit, see the Utility Programs book for your platform, included with other Sybase products.
 Starting dsedit
Starting dseditThe dsedit executable is held in the SYBASE\bin directory, which is added to your path on installation. You can start dsedit either from the command line or from the Windows Explorer in the standard fashion.
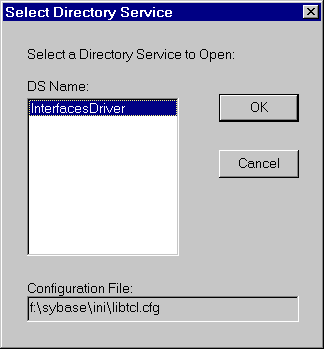
When you start dsedit, the Select Directory Service window appears.
 Opening a Directory Services session
Opening a Directory Services sessionThe Select Directory Service window allows you to open a session with a directory service. You can open a session to edit one of the following:
Any directory service that has a driver listed in the libtcl.cfg file
The interfaces file (sql.ini).
 To open a session:
To open a session: Click the local name of the directory service you want to connect to, as listed in the DS Name box, and click the OK button.
For Adaptive Server Anywhere, you should select the Interfaces Driver.
SYBASE environment variable must be set |
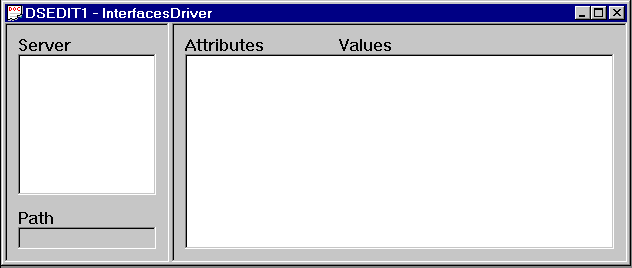
You can add, modify, or delete entries for servers, including Adaptive Server Anywhere servers, in this window.
 Adding a server entry
Adding a server entry To add a server entry:
To add a server entry: Choose Add from the Server Object menu. The Input Server Name window appears.
Type a server name in the Server Name box, and click OK to enter the server name.
The server entry appears in the Server box. To specify the attributes of the server, you must modify the entry.
The server name entered here does not need to match the name provided on the Adaptive Server Anywhere command line. The server address, not the server name, is used to identify and locate the server.
It server name field is purely an identifier for Open Client. For Adaptive Server Anywhere, if the server has more than one database loaded, the DSEDIT server name entry identifies which database to use.
 Adding or changing the server address
Adding or changing the server addressOnce you have entered a Server Name, you need to modify the Server Address to complete the interfaces file entry.
 To enter a Server Address:
To enter a Server Address: Select a server entry in the Server box.
Right-click the Server Address in the Attributes box.
Choose Modify Attribute from the popup menu. A window appears that shows the current value of the address. If you have no address entered, the box will be empty.
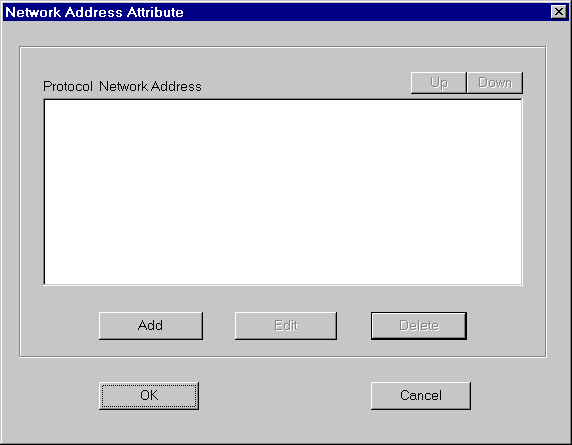
Click Add. The Network Address for Protocol window appears. Select NLWNSCK from the Protocol list box (this is the TCP/IP protocol) and enter a value in the Network Address text box.
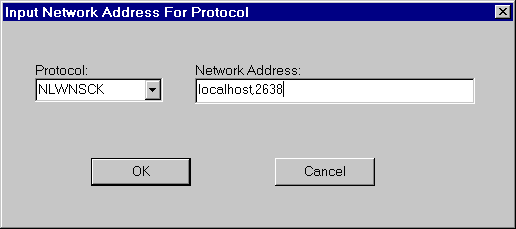
For TCP/IP addresses take one of the following two forms:
computer name,port number
IP-address,portnumber
The address or computer name is separated from the port number by a comma.
The machine on which the server is running is identified by a name or an IP address. On Windows and Windows NT you can find the machine name in Network Settings, in the Control Panel.
If your client and server are on the same machine, you must still enter the machine name. In this case, you can use localhost to identify the current machine.
The port number you enter must match the port specified on the Adaptive Server Anywhere database server command line, as described in Starting the database server as an Open Server. The default port number for Adaptive Server Anywhere servers is 2638. This number has been assigned to Adaptive Server Anywhere by the Internet Adapter Number Authority, and use of this port is recommended unless there are good reasons for explicitly using another port.
The following are valid server address entries:
elora,2638 123.85.234.029,2638
 Verifying the server address
Verifying the server addressYou can verify your network connection by using the Ping command from the Server Object menu.
Database connections not verified |
 To ping a server:
To ping a server: Ensure that the database server is running.
Click the server entry in the Server box of the dsedit session window.
Select Ping from the Server Object menu. The Ping window appears.
Click the address that you want to ping. Click Ping.
A message box appears, to notify you if the connection is successful or not. A message box for a successful connection states that both Open Connection and Close Connection succeeded.
 Renaming a server entry
Renaming a server entryYou can rename server entries from the dsedit session window.
 To rename a server entry:
To rename a server entry: Select a server entry in the Server box.
Choose Rename from the Server Object menu. The Input Server Name window appears.
Type a new name for the server entry in the Server Name box. Click OK to make the change.
 Deleting server entries
Deleting server entriesYou can delete server entries from the dsedit session window.
 To delete a server entry:
To delete a server entry: Click a server entry in the Server box.
Choose Delete from the Server Object menu.
