 User's Guide
User's Guide
 PART 5. The Adaptive Server Family
PART 5. The Adaptive Server Family
 CHAPTER 32. Replicating Data with Replication Server
CHAPTER 32. Replicating Data with Replication Server
Data replication is the sharing of data among physically distinct databases. Changes made to shared data at any one database are replicated to the other databases in the replication system.
Data replication brings some key benefits to database users.
Data is made available locally, rather than through potentially expensive, less reliable, and slow connections to a single central database. Data is accessible locally even in the absence of any connection to a central server, so that you are not cut off from data in the event of a failure of a long-distance network connection.
Replication improves response times for data requests for two reasons. Requests are processed on a local server without accessing some wide area network, so that retrieval rates are faster. Also, local processing offloads work from a central database server so that competition for processor time is decreased.
 Sybase replication technologies
Sybase replication technologiesSybase provides two replication technologies: SQL Remote and Replication Server.
SQL Remote SQL Remote is designed for two-way replication involving a consolidated database and large numbers of remote databases, typically including many mobile databases. Administration and resource requirements at the remote sites are minimal, and a typical time lag between the consolidated and remote databases is on the order of hours.
Replication Server Replication Server is designed for replication among relatively small numbers of data servers, with a typical time lag between primary data and replicate data of a few seconds, and generally with an administrator at each site.
Each replication technology has its own documentation. This chapter describes how to use Adaptive Server Anywhere with Replication Server.
 For information about SQL Remote, see the book Data Replication with SQL Remote.
For information about SQL Remote, see the book Data Replication with SQL Remote.
 Replicate sites and primary sites
Replicate sites and primary sitesIn a Replication Server installation, the data to be shared among databases is arranged in replications.
For each replication definition, there is a primary site. Changes to the data in the replication are made only at the primary site for that replication. The sites that receive the data in the replication are called replicate sites.
 Replicate site components
Replicate site componentsYou can use Adaptive Server Anywhere as a replicate site with no additional components.
The following diagram illustrates the components required for Adaptive Server Anywhere to participate in a Replication Server installation as a replicate site.
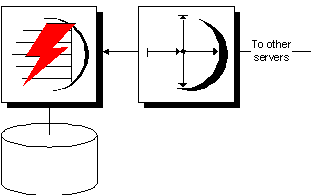
Replication Server receives data changes from primary site servers.
Replication Server connects to Adaptive Server Anywhere to apply the changes.
Adaptive Server Anywhere makes the changes to the database.
Replication Server can use asynchronous procedure calls (APC) at replicate sites to alter data at a primary site database. If you are using APCs, the above diagram does not apply. Instead, the requirements are the same as for a primary site.
 Primary site components
Primary site componentsTo use an Adaptive Server Anywhere database as a primary site, you need to use the Log Transfer Manager (LTM), or Replication Agent. The LTM supports Replication Server version 10.0 and greater.
The following diagram illustrates the components required for Adaptive Server Anywhere to participate in a Replication Server installation as a primary site. The arrows in the diagram represent data flow.
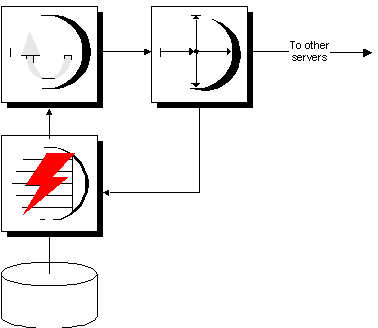
The Adaptive Server Anywhere database server manages the database.
The Adaptive Server Anywhere Log Transfer Manager connects to the database. Itscans the transaction log to pick up changes to the data, and sends them to Replication Server.
Replication Server sends the changes to replicate site databases.
